Chemical Markup Language (CML) has emerged as a powerful tool for representing and exchanging chemical data. Its intuitive syntax and comprehensive capabilities make it an indispensable resource for researchers, educators, and industry professionals alike. This comprehensive guide will delve into the fundamentals of CML, exploring its structure, applications, tools, and future prospects.
In the realm of chemical sciences, data representation and exchange play a crucial role. CML has revolutionized this process by providing a standardized and extensible framework for capturing and sharing chemical information. Its versatility and ease of use have made it a preferred choice for a wide range of applications, including molecular modeling, cheminformatics, and scientific publishing.
Chemical Markup Language (CML)

Chemical Markup Language (CML) is a standard XML-based format for representing chemical information. It is designed to facilitate the exchange and sharing of chemical data between different software applications and databases.
CML provides a comprehensive set of tags and attributes that can be used to represent a wide range of chemical information, including molecular structures, reactions, spectra, and properties. This makes it a powerful tool for managing and disseminating chemical information in a consistent and interoperable manner.
Benefits of using CML, Chemical markup language
There are several benefits to using CML, including:
- Improved data exchange: CML provides a common format for representing chemical information, which makes it easier to exchange data between different software applications and databases.
- Enhanced data sharing: CML can be used to share chemical information with colleagues and collaborators, even if they do not use the same software application.
- Increased data interoperability: CML is an open standard, which means that it is not tied to any particular software application or database. This makes it easier to integrate CML data with other data sources and applications.
- Improved data quality: CML provides a set of validation rules that can be used to ensure that data is accurate and consistent.
Structure and Syntax of CML
Chemical Markup Language (CML) follows a structured syntax to represent chemical information in a machine-readable format. It utilizes tags and attributes to define various chemical concepts and their relationships.
Tags and Attributes
CML tags enclose chemical entities, such as atoms, molecules, and reactions. Each tag has specific attributes that provide additional information about the enclosed entity. For instance, the
Applications of CML
Chemical Markup Language (CML) has gained widespread adoption in various domains, including research, education, and industry, due to its versatility and ability to represent chemical information in a structured and machine-readable format.
In research, CML is extensively used for data exchange and storage, enabling collaboration among researchers working on complex chemical projects. It facilitates the sharing of experimental data, theoretical calculations, and molecular structures, promoting transparency and reproducibility.
Education
CML plays a significant role in chemistry education by providing interactive learning materials and simulations. Students can visualize and manipulate molecular structures, explore chemical reactions, and gain a deeper understanding of chemical concepts. CML-based educational tools enhance student engagement and make learning more accessible and enjoyable.
Industry
In the chemical industry, CML finds applications in product development, safety assessment, and regulatory compliance. It enables the efficient management of chemical data, including chemical structures, properties, and reactions. CML-based tools facilitate the design of new materials, optimization of chemical processes, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Tools and Resources for CML
CML is supported by various tools and resources that facilitate the creation, editing, and visualization of CML documents. These tools enhance the accessibility and usability of CML, enabling researchers and developers to leverage its capabilities effectively.
Among the available tools are:
CML Editors
- Avogadro:An open-source molecular editor and visualizer that supports CML import and export.
- Jmol:A Java-based molecular viewer that can display CML documents.
- MarvinSketch:A commercial molecular editor that offers CML support.
CML Converters
- Open Babel:A chemical toolbox that can convert between various chemical formats, including CML.
- RDKit:A cheminformatics toolkit that provides CML import and export capabilities.
CML Validators
- CML Validator:An online tool for validating CML documents against the CML schema.
Comparison with Other Chemical Data Formats: Chemical Markup Language

CML is not the only chemical data format available. Other formats include XML and JSON, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a general-purpose markup language that can be used to represent any type of data, including chemical data. XML is a hierarchical format, which means that data is organized into a tree structure. This can make it easy to navigate and process XML data.
However, XML can also be verbose and difficult to read.
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data format that is often used to represent data in web applications. JSON is a key-value format, which means that data is organized into a set of key-value pairs. This can make it easy to access and process JSON data.
However, JSON can also be difficult to read and write.
Advantages of CML
- CML is a specialized chemical data format that is designed to represent chemical data in a structured and unambiguous way.
- CML is based on XML, which is a well-established and widely supported markup language.
- CML is an open standard, which means that it is freely available to use and implement.
Disadvantages of CML
- CML can be verbose and difficult to read, especially for users who are not familiar with XML.
- CML is not as widely supported as some other chemical data formats, such as XML and JSON.
Future Directions and Development of CML
The development of CML is an ongoing process, driven by the evolving needs of the chemical sciences community. As the field of chemistry continues to advance, CML is expected to play an increasingly important role in facilitating data exchange, collaboration, and innovation.
One of the key areas of focus for the future development of CML is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) techniques. AI and ML have the potential to revolutionize the way that we analyze and interpret chemical data, and CML is well-positioned to serve as a platform for the development and application of these technologies.
Potential Applications and Advancements of CML
The potential applications of CML in the field of chemical sciences are vast and varied. Some of the most promising areas for future development include:
- Drug discovery and development:CML can be used to represent and exchange data throughout the drug discovery and development process, from target identification to clinical trials. This can help to streamline the process and improve collaboration between researchers.
- Materials science:CML can be used to represent and exchange data on materials properties, such as structure, composition, and reactivity. This can help to accelerate the development of new materials with improved properties.
- Environmental science:CML can be used to represent and exchange data on environmental pollutants, such as their structure, toxicity, and fate in the environment. This can help to improve our understanding of the impact of pollutants on human health and the environment.
Conclusion
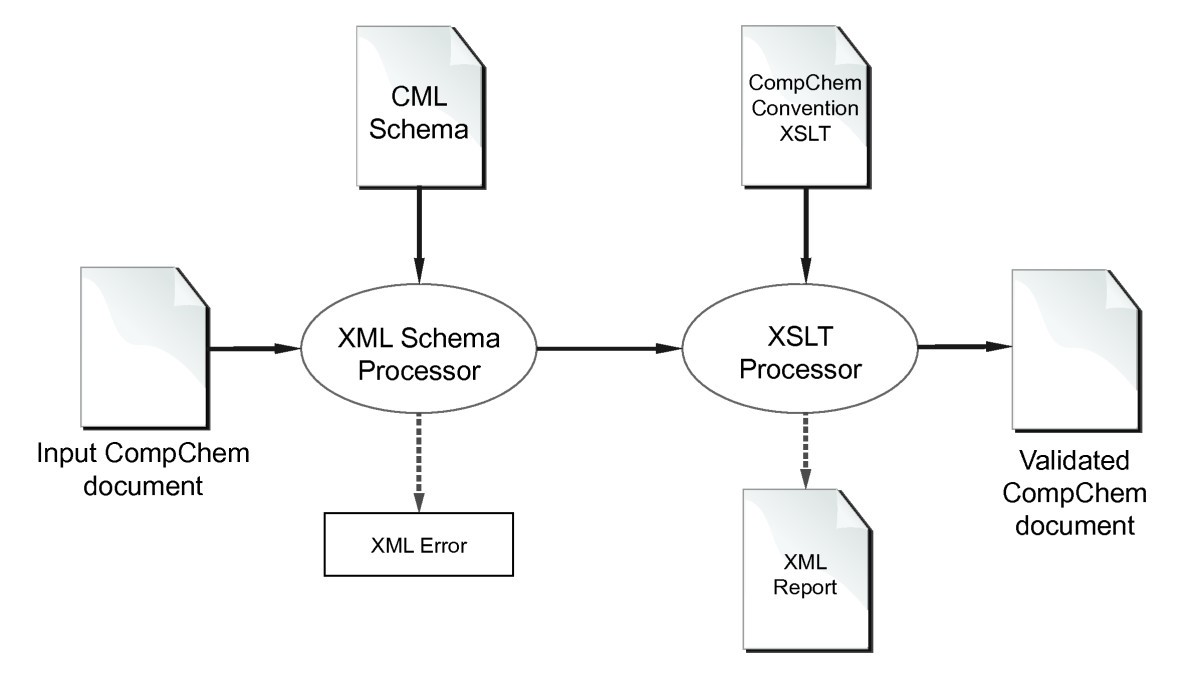
As the field of chemical sciences continues to advance, CML is poised to play an increasingly significant role. Its ongoing development and the emergence of new applications promise to further enhance its capabilities and expand its reach. Whether you are a seasoned researcher or a student embarking on your journey in chemical sciences, CML offers a powerful tool to navigate the complexities of chemical data and unlock new possibilities.
Q&A
What is Chemical Markup Language (CML)?
CML is a specialized markup language designed to represent chemical data in a structured and machine-readable format.
What are the benefits of using CML?
CML offers several advantages, including standardized data representation, enhanced interoperability, improved data visualization, and simplified data exchange.
How is CML used in research?
CML plays a vital role in research by facilitating data sharing, enabling collaboration, and supporting computational chemistry applications.
What tools are available for working with CML?
A range of tools are available, including editors, viewers, and converters, to assist in creating, manipulating, and visualizing CML documents.